In this section, you will see how to optimize production line design in the DBR77 digital twin. The implementation took place at a company manufacturing car lamps.
Case description
The plant producing lamps for passenger cars is located in southern Poland and employs 270 people working in two production shifts. The following processes take place at the plant: injection molding, painting, electroplating, assembly, labeling, quality control, and packaging. The facility covers an area of 28,000 m², and the warehouse has a size of 12,000 m².
Task description – production line design
The plant manager was tasked with designing a new production line layout that would be optimal in terms of throughput and human labor efficiency. In reality, a major challenge was to take into account the time it took for materials to move between workstations and intermediate warehouses. First and foremost, the analysis had to cover not only the physical flow of material, but also the average production time and line productivity per hour.
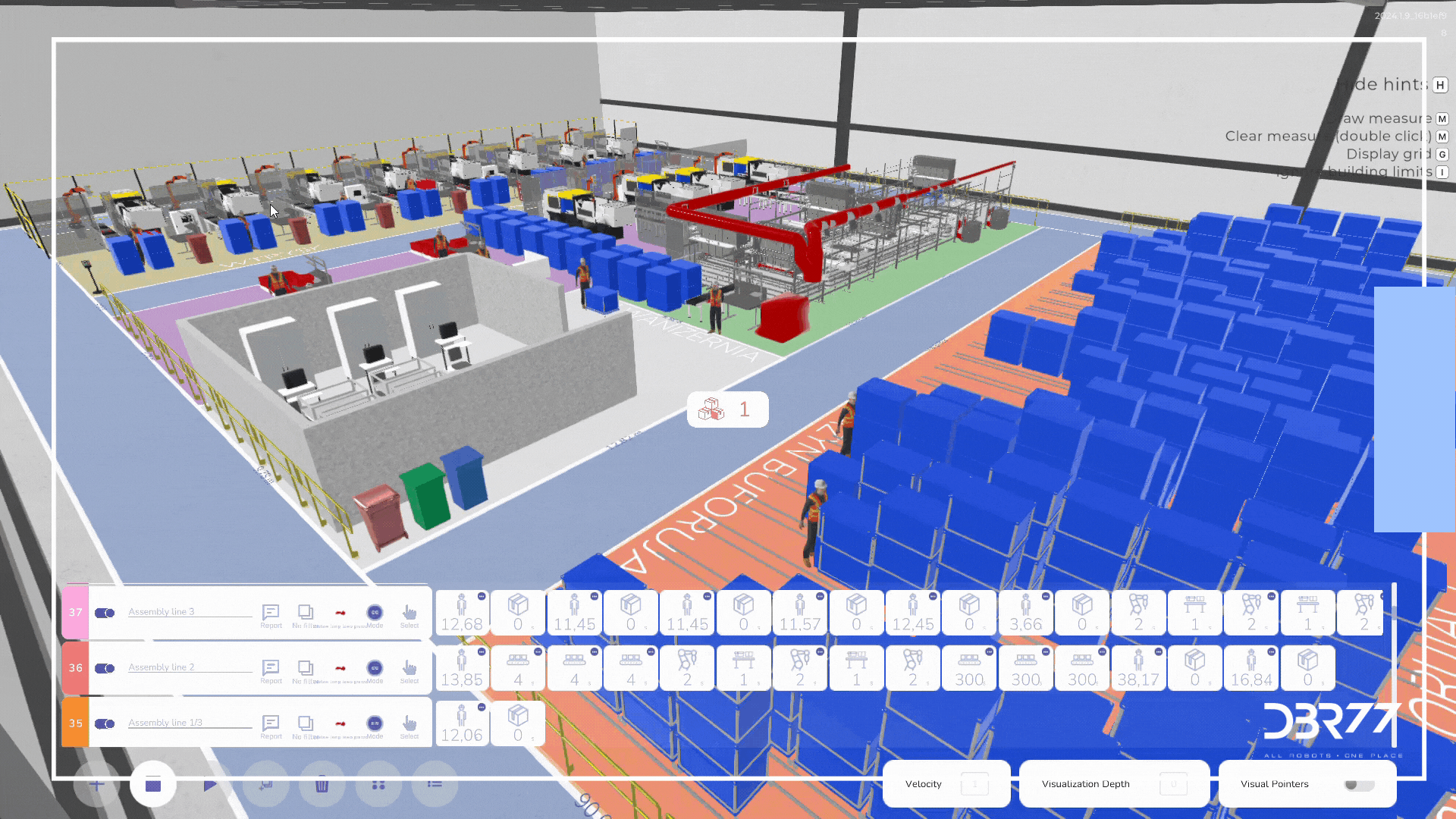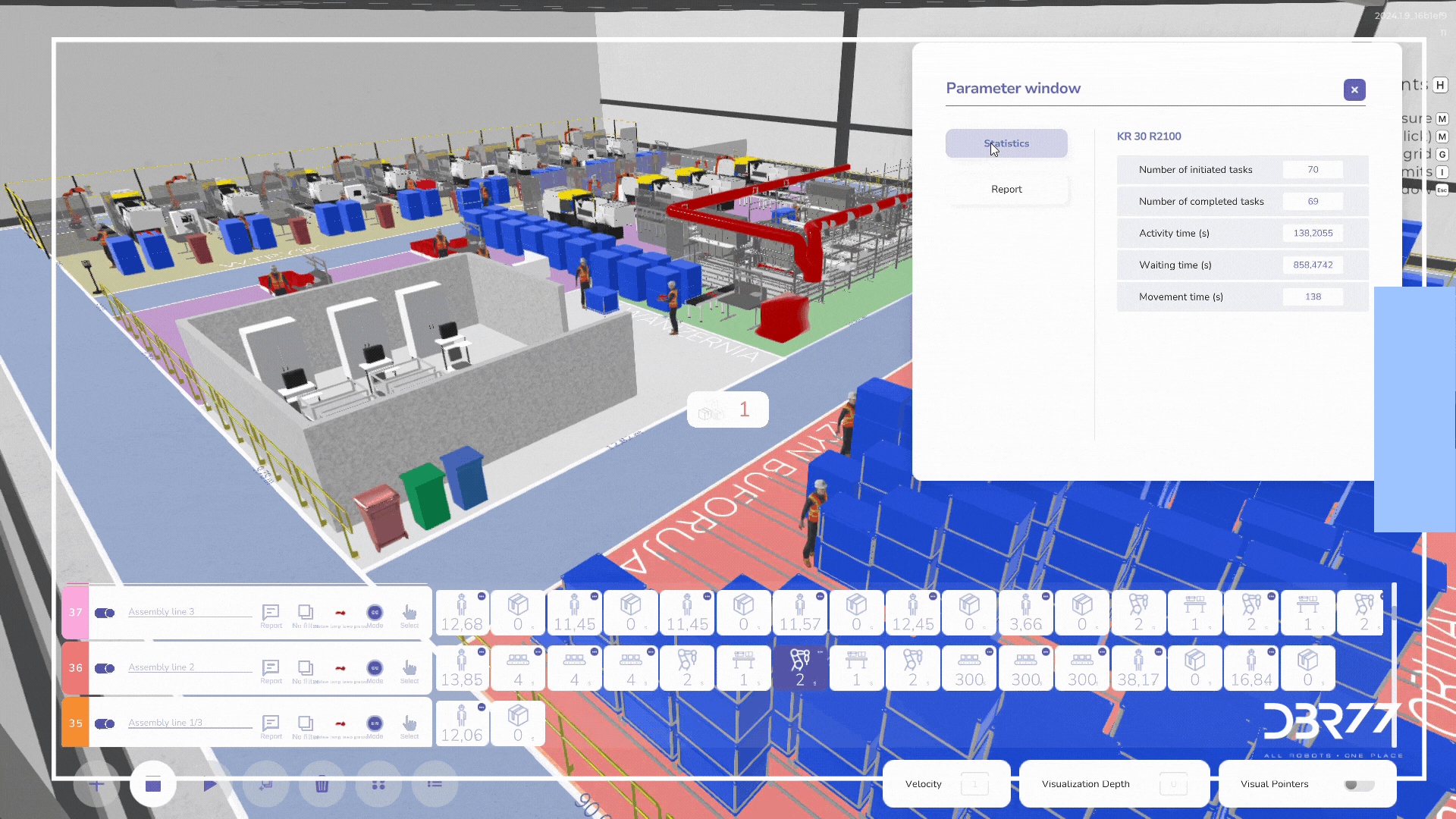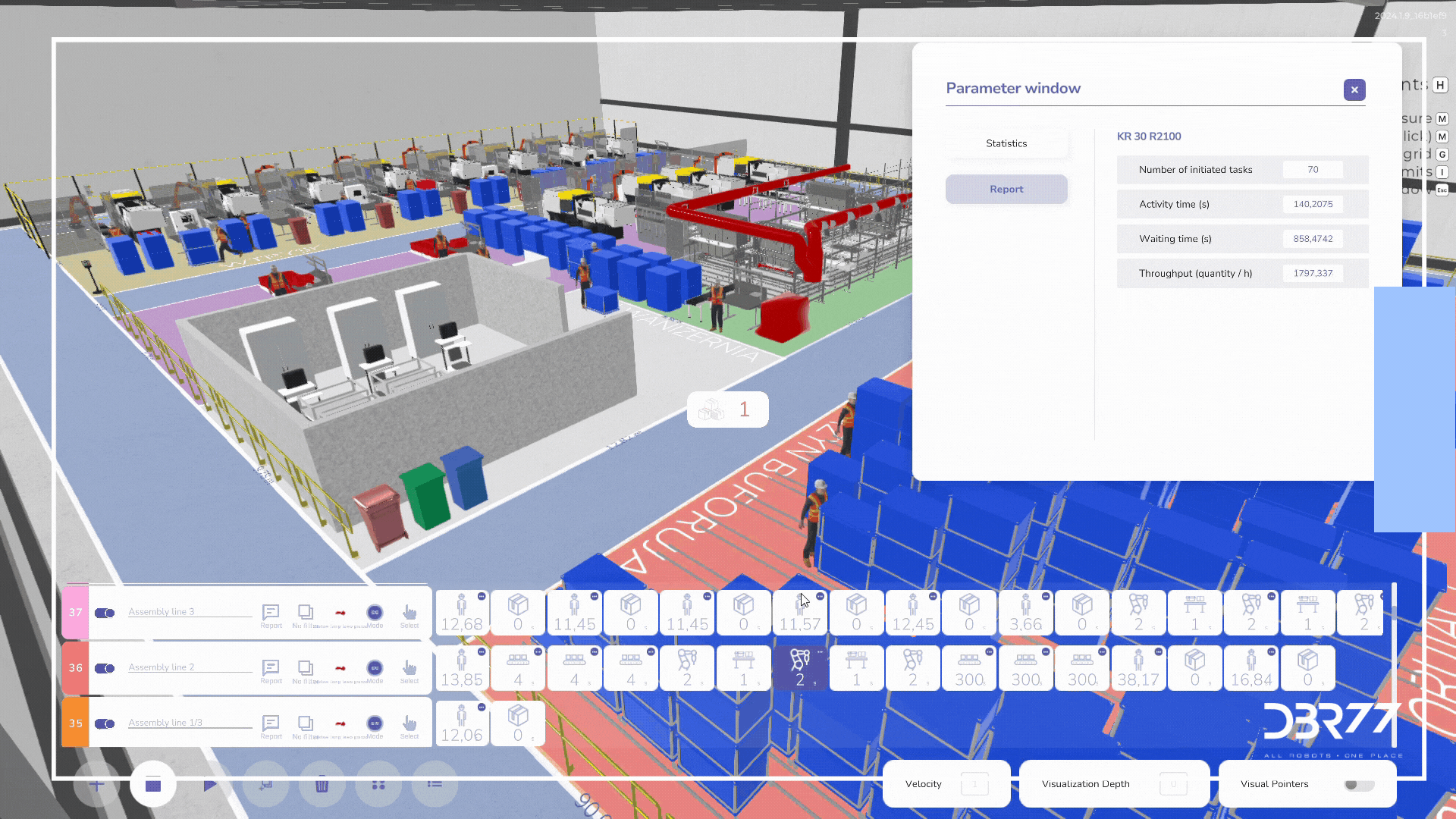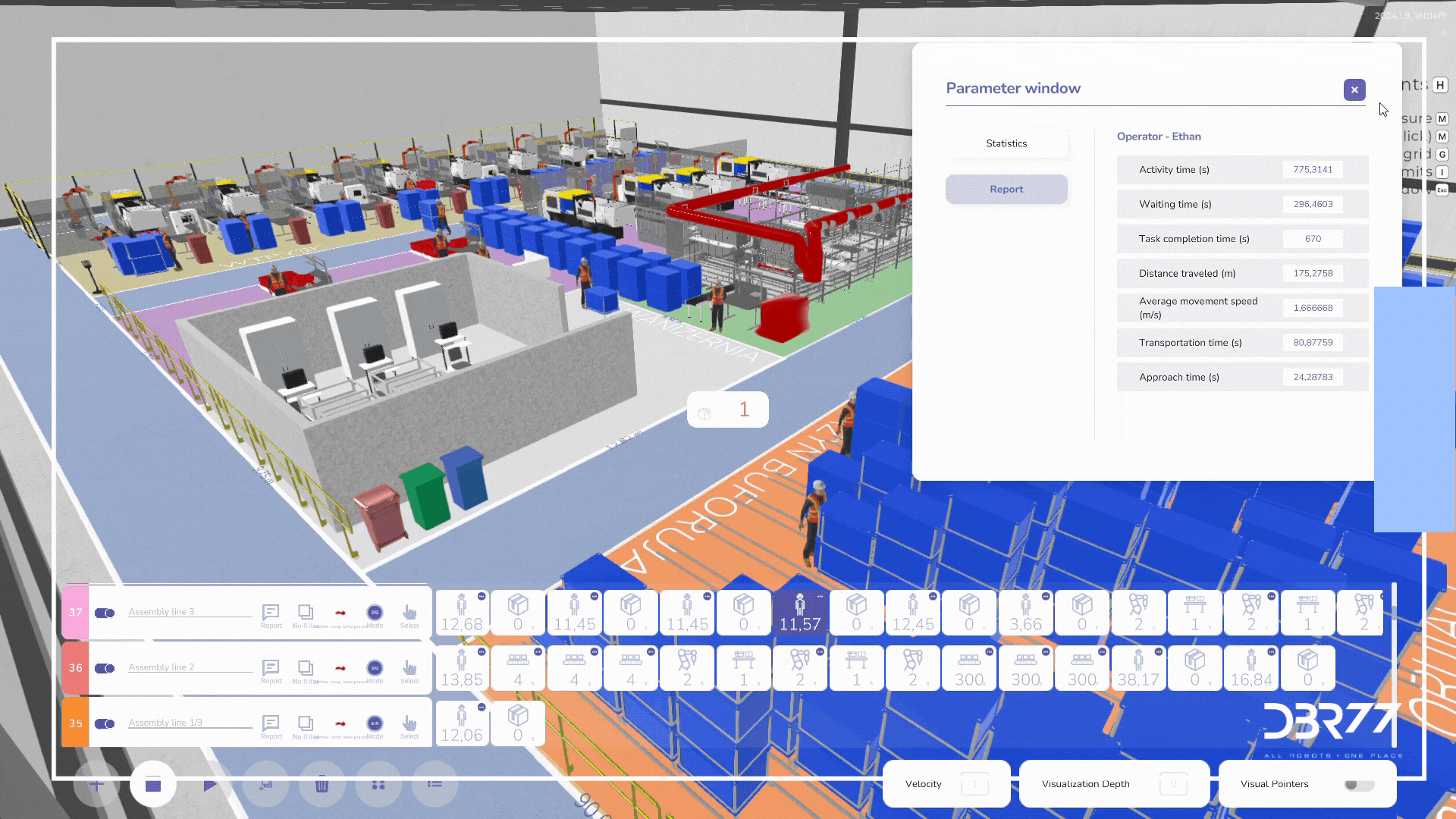
Completed work
1. Building a Digital Twin:
- Creation of a digital twin representing material flow.
- Based on the times presented in the project, working hours for the positions were determined.
- Adopting standard speeds for transport routes and describing the dynamics of braking and acceleration of trucks.
- Describe animation paths to enable animation of the entire material flow.
2. Analysis of betting options:
- Developing assumptions for three separate plant layout options.
- Comparison of material flow times and productivity for individual variants.
Results and conclusions – production line design
Of course, the most effective layout was the one that placed the buffer warehouse in the central part, between the production processes and assembly. Although the average time of material flow through the plant in this layout was not the shortest, the plant’s productivity during one day of production was on average 6% higher than in the linear production layout without an intermediate warehouse. At the same time, the loss of efficiency in alternative layouts was due to the need to wait for semi-finished products to be picked up between processes.
Benefits for the company
Thanks to the use of a digital twin, the company prepared a multi-variant dynamic analysis of the optimization and organization of the production line for a comprehensive manufacturing and assembly solution in just one week. As the analysis covered both material analysis and production capacity for the accepted order mix, it allowed for significant process improvement and increased plant productivity.
Why is Digital Twin the optimal solution?
1. Extremely fast production line prototyping:
In summary, Digital Twin enables fast and precise prototyping of a production line, taking into account the specific requirements of the available production hall. This makes it possible to quickly adapt the design to actual conditions and space constraints.
2. Material flow analysis:
A digital twin allows for accurate analysis of material flow between related process steps. This makes it possible to identify and eliminate bottlenecks and optimize internal logistics, leading to increased efficiency of the entire production process.
3. Multi-thread simulation capability:
Multithreaded simulation in a digital twin allows for simultaneous testing of various production scenarios. This makes it possible to compare different layout and process variants, ultimately leading to the selection of the most effective solution.
4. Large database of 3D models:
Digital Twin has an extensive database of 3D models, which significantly reduces the time and costs associated with creating new models. Since in most cases the available models are sufficient, this eliminates the need to supplement them and allows you to quickly start simulations.
5. Analysis of the final line design by the Management Board in VR:
The use of VR technology allows management to thoroughly familiarize themselves with the final design of the production line in virtual reality. This enables them to evaluate the proposed solutions in a more intuitive and accurate manner, which facilitates investment and operational decision-making.
Watch the entire video (switch YouTube settings to hear it in your language):
